Exceptional customer service management in today’s fast-paced business environment makes for a competitive advantage. For customer service leaders who look to empower team members, develop operations, and impact their bottom line, the data-driven approach to managing support is a one-way street.
The strategic importance of customer support means that there is a plethora of metrics to help determine success, and you probably are already measuring some of them – Net Promoter® Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), Customer Effort Score (CES), etc. – which is great! To make the most of those metrics, you need to take things one step further, figure out what insights you can gain from the data in your arsenal and how they can be used to add value to various aspects of your business.
This article will talk you through ten feedback insights that help customer service managers make informed decisions to improve a) the customer experience and b) the employee experience using the NPS as the example metric. To achieve this, we will explore the insights the NPS unravels when combined with other business-critical metrics often expressed in monetary terms.
Here we go!
NPS and Customer Lifetime Value
Today’s customer service leader is swamped with data. Using the wrong kind of data or interpreting data incorrectly might take operations in an undesirable direction.
When it comes to measuring customer experience, most quantitative metrics, such as the NPS, equalize the value of your customers, which, of course, is expected. In business terms, however, (monetary) value is not divided equally amongst your customers as, in many cases, a small percentage of customers make up for a large chunk of turnover.
Customer Lifetime Value – who is worth saving?
Consider assigning revenue to your NPS calculation to go beyond traditional NPS and gain an accurate and deeper understanding of how important customers feel about your company. This segmentation will help you identify risks and opportunities and retain high lifetime value customers. As an added benefit, looking at your NPS through customer segments can help you justify increased customer service spending. It aims to reduce high-profile client churn who expect service to be in line with what they are spending.
One goal for customer service is increasing loyalty. There must be a defined process for reacting to negative feedback. When customer service knows the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), the decision for performing a rescue attempt is a lot easier to make. It is also easier to justify the increased cost of extra contacts to top management. The transition of Customer Service from a pure cost center to a profit center becomes concrete by bringing in loyalty metrics available to support.
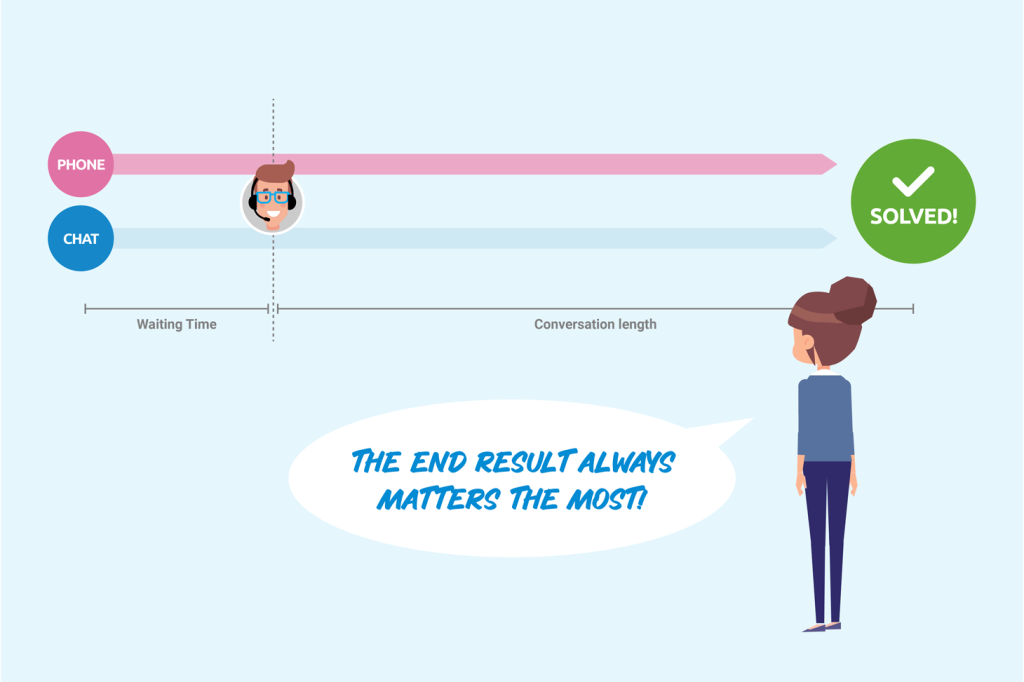
Live Support Channels: Waiting times and NPS
In customer service, every conversation is unique, but often you can find a correlation between the length of the interaction and customer satisfaction.
A common misconception among customer service organizations is that the shorter the queue time, the better the customer experience. Data, however, shows that the organization’s ability to resolve an issue at first contact is more central to a positive experience than the time waiting in a queue to be served. There is also a negative correlation between the length of the customer service interaction and what customers consider satisfactory support.
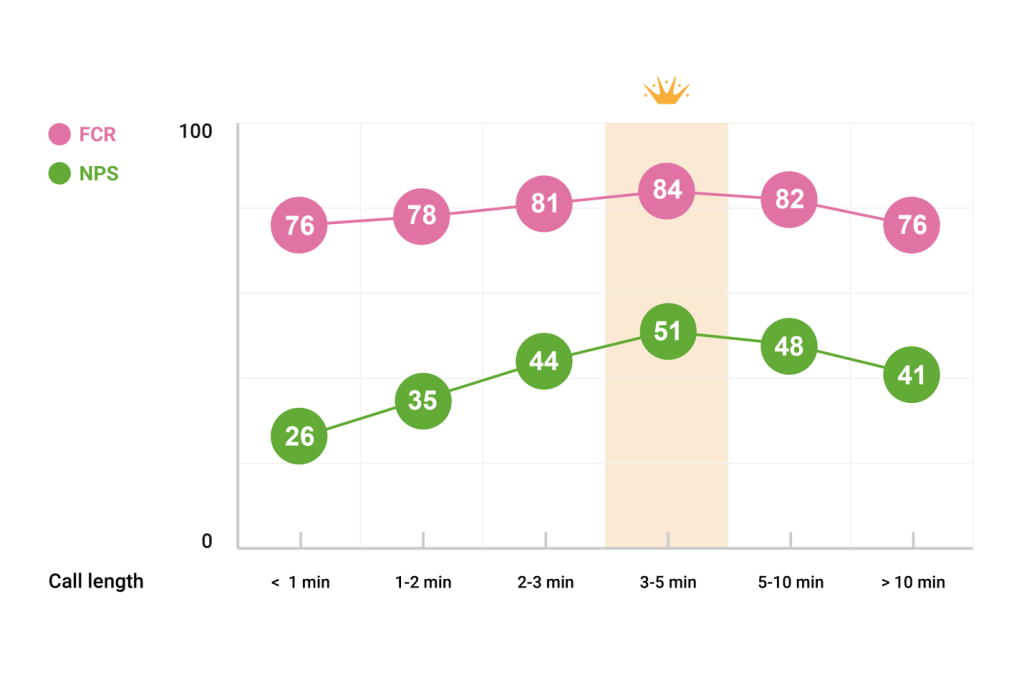
To identify best practices, analyse feedback to discover how the length of the interaction and your FCR percentage affect your NPS. This will enable you to figure out the optimal length of the interaction, allocate resources accordingly, and identify training needs.
First Contact Resolution and NPS

The beauty of First Contact Resolution (FCR) – or Resolution rate – is that it relates to the root cause that prompted the customer to contact you in the first place.
We have already discussed the importance of First Contact Resolution for the customer experience. But the strong correlation between FCR and NPS also tells another story that revolves around operational optimisation.
Most often when the customer has an issue, they reach out to you wanting to get the issue resolved. Therefore, it’s meaningful to know whether you were able to address the problem. When it comes to customer support, re-contacting customers leads to unnecessary ticket volume, availability issues, and an extra strain on operations.
If you can’t solve the cases – at first contact – at best, you’re burdening your future.
Weird as it may sound, you do not want a resolution rate that is too high. When your FCR is too good, you should automate more – no need to use agents’ time to resolve simple or routine issues. Those requests can be routed to your Help Center or a bot. After all, customer service requests and feedback data are excellent sources for learning how to improve self-service. This approach is not only cost-effective but also drives a better customer experience because customers can find answers to their questions independently, on their own terms.
What drives the FCR is your agents’ ability to resolve issues in a timely manner. Take a good hard look at your operational structure and efficiency in this context. Have you given your agents the necessary training? Do they need to submit an approval request to complete an action? Can they find all the information they need to address an issue at the same place or do they have to search through various segmented sources? Do they have the right tools to do their jobs? Do they have the decision-making power to reimburse an unhappy customer?
Your resolution rate is the gatekeeper towards answering these questions and making decisions that will make your organisation run like a well-oiled machine.
Example A
We’ve seen companies whose agents have a reimbursement authority up to a certain threshold, like 50 USD/EUR. When they factor in the internal time cost, it’s usually cheaper to give the customer what they want. This conclusion is even more evident when factoring in the estimated lifetime value for a customer segment. Unhappy customers are more likely to churn. On an aggregate level, these customer service decisions have clear effects on revenue.
Example B
A consumer service company called all their NPS detractors within 2 days and asked what went wrong. In case of a clear mistake, the agents could give out gift cards.
Remember, in every support interaction, you’re dealing with individuals with estimated customer lifetime value (CLV). Do a quick exercise. Put this monetary number above each conversation that your agents are currently having via email, chat, and phone. In some industries, an average of 30% of detractors churn. Remember your NPS numbers? How much money are you losing or making?
Only a fraction of unhappy customers eventually contact you. The ones that do are valuable sources of customer understanding. By helping them, you also help other customers who never contact you, deflecting future issues and saving future revenue.
Employee Experience and NPS
Customer service is not among the easiest jobs, as customers primarily contact you when they have problems.
Taking care of your employees is just as important as taking care of your clients. Your agents hear customers’ worries, and their daily work is often skewed in a more negative direction than on average. It is imperative to take care of your employees as they take care of your unhappy customers. Happy agents make for happy customers, and the correlation between NPS and employee NPS (eNPS) is undeniable. A customer service manager cannot afford to lose a great support agent. It costs too much time and money to find a replacement.
Recent data shows that it takes up to USD 15,000 to replace an average frontline person. What is your number?
What do you think? How much time and money would it cost to replace a current, excellent customer service agent? Fix the situation together with your employees. Fast moves pay off both from a human and financial perspective!
Decreasing employee turnover is often one of the key goals our customers strive to achieve. CS (Customer Service) functions aren’t allocated too many resources, but agent turnover can affect the bottom line through cost savings.
Building on the hypothesis that the employee experience drives the customer experience, it is important to remember to track the development of each agent’s satisfaction and pay attention to changing trends.
A good starting point when it comes to your efforts to boost employee satisfaction and reduce turnover is to understand the reasons why your customers are not satisfied with your agents’ performance. This will empower you to take the necessary steps to train accordingly and shift negative feedback into positive. Make sure to redirect that positive feedback back to your agents to boost morale, validate efforts, and celebrate success.
Understanding the key drivers of Customer Experience
Your Net Promoter® Score is just a number. The real value of it is your ability to grasp its key drivers. After all, what you need is actionable data that translate into useful insights.
Our customers at Surveypal identify the key drivers of the customer experience using predefined answer icons when asking for feedback. Satisfied customers are asked “How did we succeed?” and unhappy customers are asked “What could we do better?” and are consequently prompted to select from 4 to 6 graphical icons depicting context-relevant reasons for their score.
By doing this, they increased their open feedback ratio from 15% to over 50% and are now harvesting NPS data alongside open feedback comments to get a deeper understanding of the experience, tackle issues proactively, and avoid the same issues from arising again in the future.
Tip
CS agent Alice has worked in the team for 4 years and Mark only for 6 months. Alice is being praised for her problem-solving skills but lacks friendliness due to her slightly too harsh object-oriented nature.
Tip
Mark excels in friendliness, but his FCR rate and problem-solving feedback validate the manager’s hunch that Mark needs more product training.
People vs. Processes
It is often the case that a negative experience is not the result of inadequate support but of substandard processes or poorly thought-out product features.
If you have a gut feeling that your customer service management processes are not up to par, you can validate and quantify your suspicions by empowering your customers to select “Processes” as the main reason driving their NPS score.
At the hands of a customer service manager, this information is invaluable. It can take away a lot of the pressure agents are under, but, most importantly, it can help you justify the need to rethink or redesign processes that hinder performance and increase costs or develop product features based on customer needs and feedback.
Move towards fixing these issues by examining open feedback for these responses where the process was selected. Additionally, you can connect this aspect to your internal contact reason categories if you are categorizing your tickets.
Customer service management example
CS manager Jen notices that people complain about the process in tickets concerning product B. Open feedback often illuminates the exact reason. Jen walks up to her colleagues in product development and shows how much those issues cost. Fortunately for her, she had additionally calculated how much each ticket cost the company. Together with her colleagues, Jen puts it forward on other department’s development list. They even had the feature unprioritized in the depths of their backlog. Jen’s input was just the prioritization validation they had been waiting for, and the fix gets taken under construction.
Customer Service Volume, Resources, and NPS
By comparing customer service volume and NPS per agent, you can get the overall picture.
There is a lot to be discovered when comparing customer service volume and NPS per agent. A high number of solved tickets in conjunction with a low NPS can lead to customers recontacting your support. This will add to the volume of your customer care requests and limit your support availability. On the other hand, a high number of solved tickets alongside a high NPS, are indications that you might have an agent in your team that performs exceptionally well. This should make you consider ways to share their competencies with the rest of the team.
Moreover, the trend lines of total resolved tickets and NPS will paint an accurate picture of the relation between CS volume and resourcing and the overall quality of the customer experience. Let’s say your ticket volume has increased 20–30% during Q1 and Q2. In these kinds of exceptional periods, this mentioned overall viewpoint shows how well you’ve managed to handle the pressure.
Again, CX data like the NPS is not to be analyzed in silos but alongside other functions’ KPIs and, more importantly, with monetary business metrics like Customer Lifetime Value.
NPS across customer service channels and Reasons for Contacting
Being aware of your channel performance helps you develop operations towards a well-performing omnichannel contact center.
Understanding service channel performance will give you actionable insights to develop operations towards exceptional omnichannel support.
The service channel is a key parameter, a viewpoint from which you should look at your customer experience. Start by looking at your NPS per channel. Compare it to your resolution rate, and contact reasons to uncover why some channels perform better than others. Use this information to manage the customer’s journey towards receiving support, market the right communication channels to the right customers, and develop tools such as self-service posts, etc. to ensure a wonderful experience.
Drilling down into the reasons your clients contact your support is also imperative towards better omnichannel support. If you get requests that have to do with simple, mundane issues, reroute the customer to a chatbot or your Help Center. Self-service and chat are usually on top of the priority channel list due to their internal efficiency for the company. You should make sure that you’re able to deliver a delightful experience on those channels. Otherwise, working on improving internal efficiency isn’t sustainable and might lead to higher ticket volumes and churn.
If your requests for customer care are more complex or technical, make sure your agents have received appropriate training to handle them.

Upselling and Cross-selling in Customer Service
Traditionally, customer service and customer service management have been about solving problems and providing service.
Typically, people working in customer service are service-minded and empathic individuals. Some might think that trying to sell in customer service negatively impacts the customer experience.
Data tells a different story. Understanding and listening to your customers when they talk to you plays a crucial role. Customers who become aware of new services or products at the right moment report a better customer service experience. That’s because when you solve a customer’s problem, they are more willing to hear about other products that also have problem-solving capabilities.
Example
A customer is having connectivity issues with his internet connection and calls operator customer service. An agent can propose a solution that benefits the customer and offer a cyber security add-on that you get for free for the first three months. Clients who give customer service feedback are redirected to the e-commerce site with a discount code. The customer gets some value from providing feedback, and the company gets a sales opportunity.
From a leadership point of view, it is beneficial to know how add-om sales affect customer service quality. In many cases, upselling and cross-selling can increase productivity and transform your support from a cost to a profit center.
AI in Customer Service
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be a great additional asset in providing you with insights from a vast amount of data that you would never have time to dig through yourself manually.
One of the greatest benefits of AI in customer service is it can provide a vast amount of data automatically. For example, you can spot deviations in waiting times in certain types of support requests. When you know this, you’re left with uncovering the reason and taking the necessary steps to course correct.
Sentiment analysis on open feedback
Another use case of CX data is understanding your open feedback efficiently. Sentiment analysis is a good starting point.
With sentiment analysis, you can categorize based on product or contact reason which themes give you positive feedback. For example, you get to see the top 3 contact reasons which generate the most negative feedback. When you know this, you can filter and organize these themes based on customer issues and open feedback.
Example
Customer Service Manager Jill had a rough month. Her company released a new product last month, and this move generated contacts to customer service over expectations. Her team was struggling for many days, and the ticket backlog kept growing. AI revealed that open feedback on the new product had three times the number of negative comments compared to negatives on average.
At this point, Jill was quick to dig into the data and go through the given reasons (predefined icons, check section 5) and open feedback. Most customers repeatedly complained about how long it took to resolve the problem. Customers had to wait an unreasonably long time before receiving help. Jill already had argued with product development based on her hunch on how the new product over-employed them.
With the solid numbers she found, she could quantify the effect and base her arguments on numbers. This was something that could not happen again. Product development needs to have efficient collaboration with customer service in advance to create enough self-service content.
Lack of communication creates extra internal workload and a bad customer experience. Some detractors might not continue using the product as the start was clumsy and revolving issues took too much time. Jill knows that for each detractor that contacted CS six people faced the same problems but did not contact support.
Hence, the lost customer lifetime value is x 6
Did you like the post?
You might also like:

Surveypal
Everything you need to lead and improve your customer experience. Learn more at surveypal.com, or